Uterine Fibroids: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
- Adithya Santosh Kumar
- Mar 2, 2022
- 2 min read
What are Uterine Fibroids?
Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths made up of connective and muscle tissues that appear in the wall of the uterus. Fibroids can develop as a single tumor, or multiple fibroid growths can line the uterine walls. They can be as small as an apple seed or as big as a tennis ball. In extreme cases, they may even exceed these sizes!
What causes Fibroids and why we must raise awareness about them?
Researchers are often stumped on the origin of fibroids. They are generally linked to the hormones progesterone and estrogen, as well as genetics. As hormone production slows down during menopause, fibroids usually shrink. Diets consisting of high portions of red meat and not enough green vegetables have been associated with a higher risk of developing fibroids.
Approximately 40 percent to 80 percent of women experience fibroid growths. They become more common as women age and are recurrently found in women in their 40’s and 50’s. Studies have indicated that there exists a hereditary component, and thus having a family member with fibroids, can increase your risk.
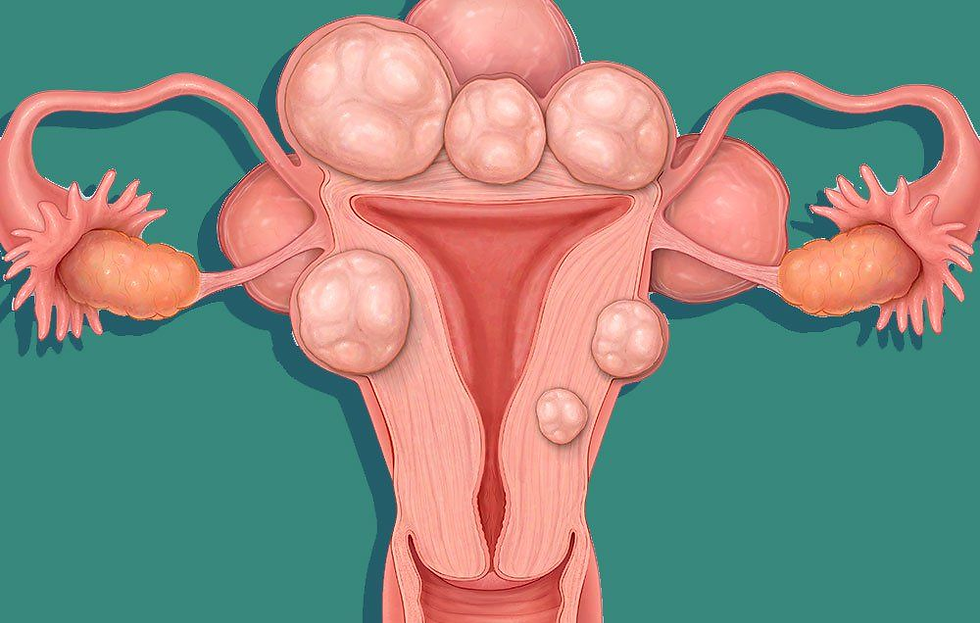
Symptoms related to Fibroids
Most women are asymptomatic when it comes to fibroids. However, women with fibroids have reported:
Enlargement of lower abdomen and weight gain
Back Pain
Heavy Bleeding as well as painful periods
Fertility complications
Urinary issues
Depression and anxiety due to the unexpected symptoms
Why Fibroids must be treated and the various methods of treatment
If left untreated, harmful fibroids rapidly continue to grow in the uterus, both in size and number. This can lead to an increase in bleeding, accompanied by cramping and in severe cases, anaemia due to the high blood loss. So here are some procedures that one can follow to treat fibroids:
Watch and Wait: This method is recommended to someone with fibroids who are asymptomatic or experience mild symptoms. Since fibroids tend to disappear on their own, it is better to avoid treatment unless absolutely necessary. Medications such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen are usually prescribed for mild symptoms. Doctors also recommend taking an iron supplement in the case of heavy bleeding during periods to negate the risk of getting anaemia.
Hysterectomy: Hysterectomy is usually recommended to women who have symptomatic fibroids. This process involves the surgical removal of the uterus, thus ending all the problems related to uterine fibroids. However, due to the removal of the uterus, this treatment isn’t optimal if the woman wants to bear children.
Myomectomy: Myomectomy is an intricate surgery to remove the harmful fibroid growths while leaving the healthy uterine tissues intact. It is recommended to women who wish to have children after their treatment. However, unlike hysterectomy, new fibroids can continue to grow post myomectomy treatment.
Fibroid Embolization: This non-surgical method selectively blocks out blood vessels that supply blood to the fibroid. The blood vessels are injected with tiny plastics or gel to block the flow of blood.
Fibroids are an extremely volatile growth. They can either be completely harmless or lead to severe complications. With proper education and increasing awareness around fibroids, women can feel less anxious about their fibroids and find the necessary treatment to remove them.



Comments